

This gene is involved in chromosomal translocations, resulting in different fusion gene products, such as TMPSSR2-ERG and NDRG1-ERG in prostate cancer, EWS-ERG in Ewing's sarcoma and FUS-ERG in acute myeloid leukemia. It also regulates hematopoesis, and the differentiation and maturation of megakaryocytic cells. This protein is required for platelet adhesion to the subendothelium, inducing vascular cell remodeling. It contains an ETS DNA-binding domain and a PNT (pointed) domain which is implicated in the self-association of chimeric oncoproteins.

The protein encoded by this gene is mainly expressed in the nucleus. All members of this family are key regulators of embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, inflammation, and apoptosis. Database of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (dbSNP)įull Name ETS transcription factor ERG provided by HGNC Primary source HGNC:HGNC:3446 See related Ensembl:ENSG00000157554 MIM:165080 Gene type protein coding RefSeq status REVIEWED Organism Homo sapiens Lineage Eukaryota Metazoa Chordata Craniata Vertebrata Euteleostomi Mammalia Eutheria Euarchontoglires Primates Haplorrhini Catarrhini Hominidae Homo Also known as p55 erg-3 Summary This gene encodes a member of the erythroblast transformation-specific (ETS) family of transcriptions factors.Database of Genomic Structural Variation (dbVar).Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM).

Database of Genotypes and Phenotypes (dbGaP).Structure (Molecular Modeling Database).
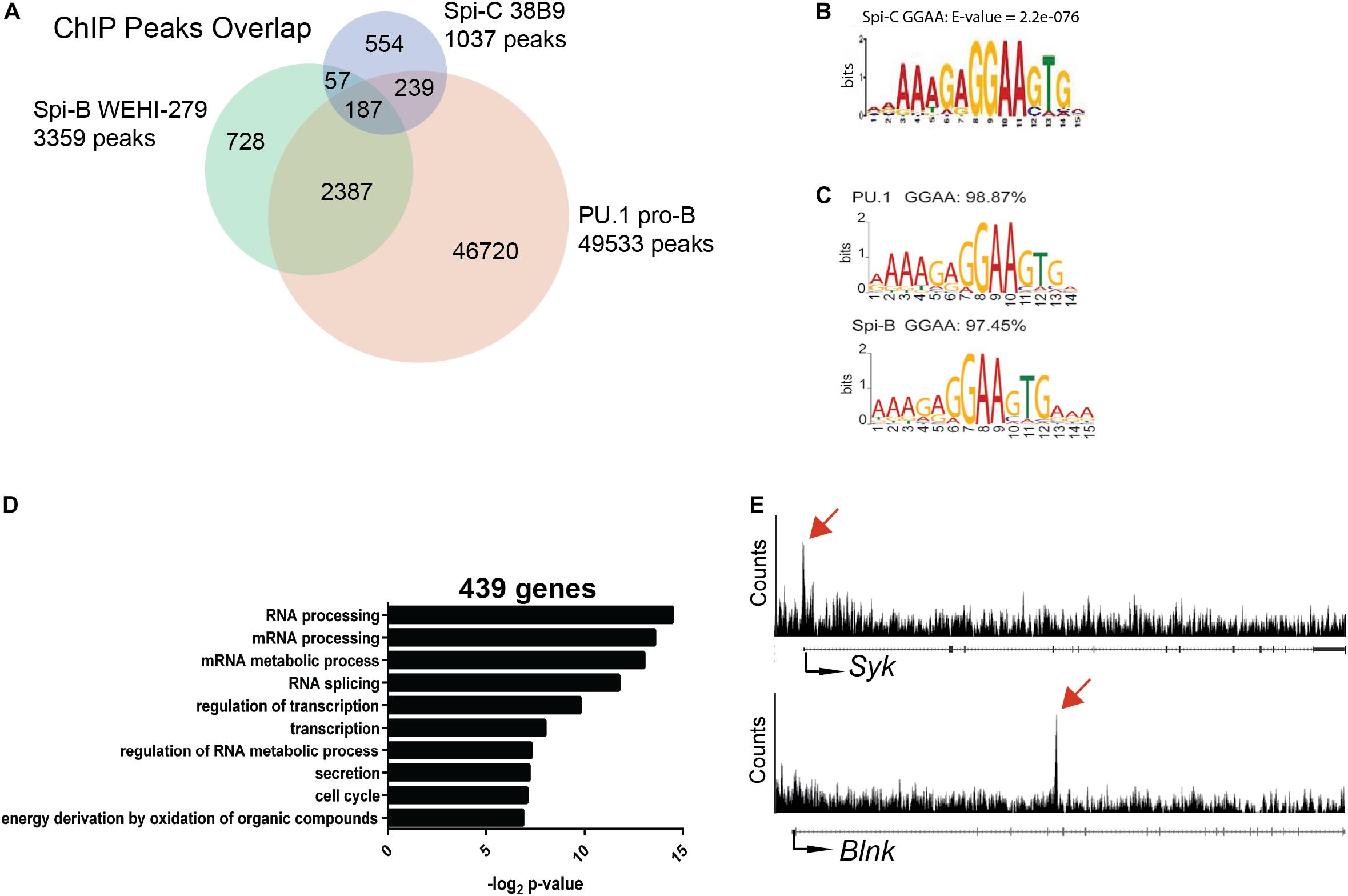 Conserved Domain Search Service (CD Search). BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool). Homologies within the Ets domains and their localization divide the Ets superfamily into related classes, as shown in Table 1. The DNA binding activity of several Ets factors (Ets-1, Ets-2, SAP-1, Elk, Net, and ERM) is also subject to intramolecular autoinhibition by sequences flanking the Ets domain (2, 4). More divergent sequences are present in loops and turns and are thought to confer binding specificity (4). The most highly conserved residues are those located in the hydrophobic core or invariant arginines and lysines that make contacts with specific bases or the phosphate backbone, respectively (8). The family is defined by the highly conserved Ets domain, comprising 84-90 amino acids folded into a novel DNA binding structure, consisting of three alpha helices and a four-stranded antiparallel beta sheet forming a winged helix-turnhelix motif (7). The founding member of the Ets family, v-Ets, was discovered some 15 yr ago as a fusion protein with gag and myb in the avian erythroblastosis retrovirus E26 (Ets = E twenty-six specific) (5, 6). The Ets gene family has not been detected in plants, fungi, or protozoans (4). At least 40 different Ets sequences have been identified in both vertebrates and invertebrates, representing approx 25 distinct proteins. The Ets transcription factors represents a novel structural class of transacting proteins that have important roles in development, proliferation, and differentiation of cells and in oncogenic transformation (1–3).
Conserved Domain Search Service (CD Search). BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool). Homologies within the Ets domains and their localization divide the Ets superfamily into related classes, as shown in Table 1. The DNA binding activity of several Ets factors (Ets-1, Ets-2, SAP-1, Elk, Net, and ERM) is also subject to intramolecular autoinhibition by sequences flanking the Ets domain (2, 4). More divergent sequences are present in loops and turns and are thought to confer binding specificity (4). The most highly conserved residues are those located in the hydrophobic core or invariant arginines and lysines that make contacts with specific bases or the phosphate backbone, respectively (8). The family is defined by the highly conserved Ets domain, comprising 84-90 amino acids folded into a novel DNA binding structure, consisting of three alpha helices and a four-stranded antiparallel beta sheet forming a winged helix-turnhelix motif (7). The founding member of the Ets family, v-Ets, was discovered some 15 yr ago as a fusion protein with gag and myb in the avian erythroblastosis retrovirus E26 (Ets = E twenty-six specific) (5, 6). The Ets gene family has not been detected in plants, fungi, or protozoans (4). At least 40 different Ets sequences have been identified in both vertebrates and invertebrates, representing approx 25 distinct proteins. The Ets transcription factors represents a novel structural class of transacting proteins that have important roles in development, proliferation, and differentiation of cells and in oncogenic transformation (1–3).








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
